Smart Lighting Systems: DIY Installation and Advanced Automation in 2026
Smart Lighting Systems: DIY Installation and Advanced Automation in 2026
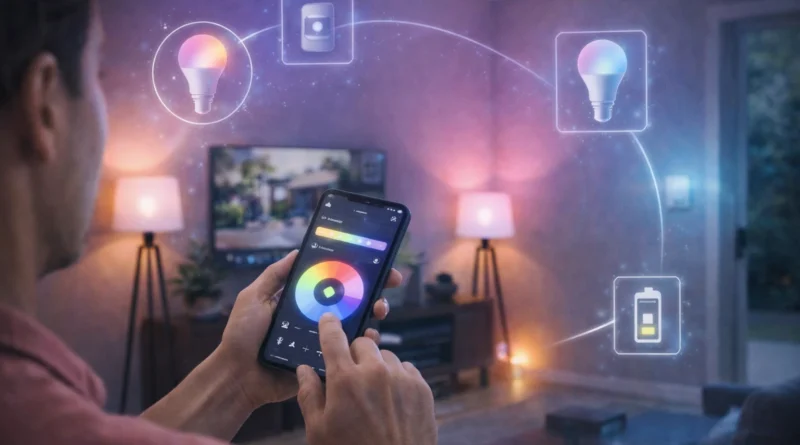
Smart lighting is one of the easiest yet most impactful upgrades for a smart home. Beyond simply turning lights on or off, advanced lighting systems let you automate schedules, adjust brightness and color, integrate with other devices, and save energy while enhancing ambiance. In my Tunis apartment, connecting smart bulbs and motion sensors allowed me to walk into a room at night and have lights turn on automatically, while also reducing electricity usage noticeably. This guide covers hardware, software, installation, automation ideas, AI integration, troubleshooting, and expansion tips for a fully automated lighting system.
1. Understanding Smart Lighting
Smart lighting enables automated schedules based on time, occupancy, or natural light, integration with other smart devices like thermostats, security systems, and entertainment, remote control via smartphone or voice assistant, and energy efficiency. Modern smart bulbs offer dimming, color control, and scene creation for mood lighting. From real experience, having “reading mode” scenes set up allowed me to relax in the evening without manually adjusting lights.
2. Required Hardware Components
Essential components include smart bulbs (Wi-Fi or Zigbee, e.g., Philips Hue, LIFX, TP-Link Kasa), smart switches to replace traditional switches (Lutron Caseta, TP-Link Kasa), optional hub for Zigbee devices or complex automations, motion sensors to trigger lights, and smart plugs to control lamps or non-bulb lighting. Tip: verify that bulbs, switches, and sensors are compatible with your chosen hub or automation platform. In practice, mismatched bulbs caused connectivity delays until I standardized all devices on the same hub.
3. Software Platforms
Popular platforms include Home Assistant (highly customizable), OpenHAB (modular for advanced users), Philips Hue App (simple setup for Hue bulbs), and Node-RED (visual programming for complex flows). Setup involves installing the hub or platform, connecting bulbs, switches, and sensors, creating automation routines, testing, and refining scenarios. Real-Life Tip: start small with a single room to ensure routines work as expected before scaling.
4. Automation Ideas
Automation scenarios include scheduled lighting (turn lights on/off at specific times), motion-triggered lights (automatic activation when entering a room), sunrise/sunset adjustments (automatic brightness or color changes), and voice control with Alexa, Google Assistant, or local AI assistants. Advanced routines can integrate lighting with security systems, energy management, or entertainment. In my setup, combining living room lights with motion sensors and TV activity created an immersive home theater experience.
5. AI Integration
AI enhances smart lighting by predicting lighting preferences, adjusting lights automatically for mood or activity, integrating with smart cameras to detect occupancy or gestures, and providing energy-saving suggestions. Privacy Tip: running AI locally keeps all data private. Personally, AI learned to dim bedroom lights gradually in the evening, helping improve sleep habits.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common problems include bulbs not connecting (check Wi-Fi/Zigbee coverage and firmware), switches not responding (verify wiring and hub recognition), and automation rules not triggering (review settings and connectivity). Maintaining a device list and logs helped me quickly identify a disconnected sensor that blocked a whole room’s automation.
7. Expanding Your Smart Lighting System
Expand by adding more bulbs and smart switches, integrating motion sensors for energy efficiency, connecting to entertainment systems for synchronized lighting, and creating multi-room scenes and schedules. Tip: focus on frequently used areas first for maximum impact.
8. Safety Considerations
Follow electrical safety rules during switch or wiring installation, use certified smart devices, keep firmware updated, and secure your Wi-Fi network. From real experience, using a secured Wi-Fi network prevented unauthorized access to my smart lighting routines.
9. FAQ – DIY Smart Lighting
Q1: Can I mix brands of bulbs and switches?
A: Yes, if they are compatible with your hub or platform.
Q2: Do I need programming skills?
A: Basic automations require no coding; advanced routines may require scripting in YAML or Node-RED.
Q3: How much energy can I save?
A: Automation can reduce energy usage by 20–40% depending on habits and setup.
Q4: Can AI control color and brightness automatically?
A: Yes, AI can adapt lighting based on time, activity, or preferences.
Q5: Is remote control possible?
A: Yes, all connected bulbs and switches can be controlled via mobile apps or voice assistants.
Conclusion
DIY smart lighting improves convenience, energy efficiency, and ambiance. With compatible hardware, automation routines, and AI integration, you can create a responsive, enjoyable, and future-ready home environment. Start with one room, test routines, and gradually expand for maximum impact.