Smart Home Security Systems: DIY Installation and Automation in 2026
Smart Home Security Systems: DIY Installation and Automation in 2026
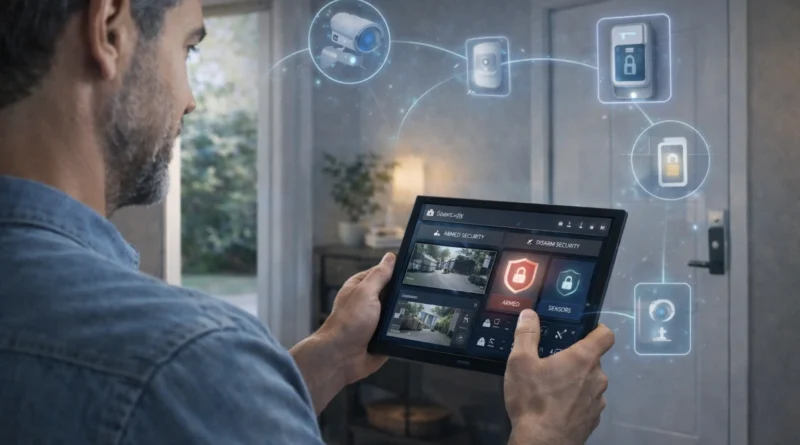
Home security is a top priority for homeowners, and DIY smart home technology allows you to build a reliable, customizable system. A smart security setup integrates cameras, sensors, alarms, and automation to protect your home while providing real-time insights and control from anywhere. In my own apartment in Tunis, installing a combination of indoor/outdoor cameras, motion sensors, and smart locks allowed me to monitor entrances remotely and receive instant notifications. Within the first week, I could detect package deliveries and unusual activity, giving peace of mind and enhanced safety. This guide covers hardware, software, setup, AI integration, automation, troubleshooting, and best practices for a fully automated home security system.
1. Understanding Smart Home Security
A smart security system connects multiple devices into one automated platform. Typical components include surveillance cameras for indoor and outdoor monitoring, door and window sensors to detect unauthorized entry, motion detectors for activity alerts, smart locks for controlled access, and alarms/notifications for immediate alerts. Benefits include peace of mind, remote monitoring, and automated responses to security events. From my experience, having cameras linked to motion-triggered lighting prevented potential security incidents in dark areas outside my home.
2. Required Hardware Components
Building a DIY smart home security system requires: a central security hub (e.g., Ring, Abode, or Home Assistant Hub), indoor/outdoor IP cameras with night vision, door/window contact sensors, motion detectors, smart locks like August, Yale, or Schlage, optional alarm sirens for audible alerts, and a touchscreen for direct control. Tip: choose hardware fully compatible with your automation platform to avoid integration issues. In practice, mismatched devices caused delayed alerts until I standardized brands on the same hub.
3. Software Platforms
Popular platforms include Home Assistant (open-source, device integration, automation), OpenHAB (advanced rules for security), Domoticz (lightweight, simple for small setups), and dedicated apps provided by specific hubs. Setup involves installing hub software, pairing cameras, sensors, and locks, testing connectivity, and configuring automation rules for alerts, schedules, and emergency routines. Real-life Tip: start with basic monitoring and gradually implement complex automations to ensure reliability.
4. Automation Scenarios
Smart security automation can include automatic arming/disarming based on schedule or geolocation, integrating lights to turn on when motion is detected at night, triggering cameras when doors/windows open, and sending emergency notifications to your phone. In my own home, integrating motion sensors with porch lights prevented potential intrusions during nighttime. Tip: test each routine individually before combining multiple automations to avoid conflicts.
5. AI Integration
AI enhances home security by detecting unusual activity, providing facial recognition for authorized individuals, analyzing patterns for predictive alerts, and supporting voice command control. Privacy Tip: running AI locally ensures sensitive footage remains on your network. In real use, AI differentiated between pets and humans, drastically reducing false alarms in my apartment.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common problems include cameras not streaming (check Wi-Fi and settings), unresponsive sensors (replace batteries and ensure pairing), and automation not triggering (review rules and device status). Maintaining a system log helps quickly identify and resolve issues. From experience, even a single misconfigured motion sensor can block multiple automation routines until corrected.
7. Expanding Your Security System
You can expand coverage by adding more cameras or sensors, integrating smart locks for remote access, combining lighting with AI routines for full automation, and adding battery backups to maintain operation during outages. Practical Tip: prioritize critical entry points first before expanding to secondary areas.
8. Safety and Best Practices
Secure your network with strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, update firmware/software regularly, and periodically test all devices. In my setup, enabling secure cloud access and local backups prevented data loss during a temporary network outage.
9. FAQ – DIY Smart Home Security
Q1: Can I integrate older devices?
A: Yes, with compatible hubs or adapters.
Q2: Do I need technical expertise?
A: Basic installation is easy; advanced automation may require familiarity with the platform.
Q3: Is remote monitoring secure?
A: Yes, if using encrypted connections, VPNs, or secure apps.
Q4: Can AI reduce false alarms?
A: Yes, AI can distinguish between humans, pets, and other movement to minimize false triggers.
Q5: What is the cost?
A: Depending on devices and AI integration, $300–$1000 for a comprehensive DIY system.
Conclusion
A DIY smart home security system gives homeowners peace of mind, control, and automation. By combining compatible hardware, AI integration, and practical planning, you can create a reliable, future-ready security system. Start with essential devices, gradually expand, and test routines in real-life conditions for maximum safety and efficiency.