DIY Smart Energy Monitoring: Optimize Your Home Power Usage in 2026
DIY Smart Energy Monitoring: Optimize Your Home Power Usage in 2026
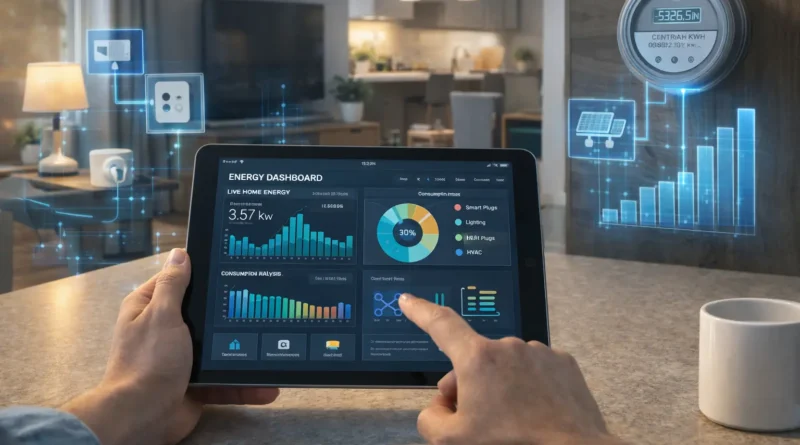
Smart energy monitoring allows homeowners to track electricity consumption, optimize energy usage, and reduce costs. In my own apartment in Tunis, installing a DIY energy monitoring system helped me identify high-energy appliances, schedule usage, and save nearly 25% on electricity within the first two months. By integrating smart plugs, meters, and AI routines, you can gain real-time insights and automate energy-saving strategies across your home. This guide covers hardware, software, setup, AI integration, automation ideas, troubleshooting, and expansion strategies.
1. Understanding Smart Energy Monitoring
Smart energy monitoring enables real-time tracking of electricity consumption, identification of high-energy devices, automated energy-saving routines, and integration with smart plugs, lighting, and HVAC systems. Benefits include cost savings, reduced carbon footprint, and improved efficiency. Human Insight: I discovered that my old fridge and water heater were responsible for almost half of my energy bills, which allowed me to automate their schedules and reduce waste.
2. Required Hardware Components
You will need smart energy meters (circuit or device-level), smart plugs with energy monitoring, a hub or single-board computer (Raspberry Pi, Home Assistant, or compatible hub), optional voltage/current sensors for advanced monitoring, and connectivity modules (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave). Pro Tip: Ensure that meters and plugs are compatible with your hub or automation platform for accurate reporting and easy integration.
3. Software Platforms
Popular software platforms include Home Assistant (integrates multiple monitoring devices and dashboards), OpenHAB (advanced automation and analytics), Node-RED (custom monitoring flows and alerts), and vendor-specific apps for simplified monitoring. Setup Steps: Install smart meters or plugs, connect devices to your hub, configure dashboards to visualize consumption, and create alerts or automation routines to optimize energy usage. Human Experience: Visual dashboards helped me instantly see peak usage times and adjust routines to save energy without sacrificing comfort.
4. Automation Ideas
Energy automation can include scheduling devices to turn off during peak hours, dimming lights automatically, reducing HVAC usage when rooms are unoccupied, sending consumption alerts, and using AI suggestions to determine the best times to run appliances. Practical Tip: I programmed my assistant to turn off the laundry machine at night and start it during cheaper electricity hours, which noticeably lowered my bills.
5. AI Integration
AI enhances energy monitoring by predicting consumption patterns, suggesting automation for efficiency, detecting unusual spikes for safety, and optimizing heating, cooling, and lighting automatically. Privacy Tip: Run AI locally or encrypt data to keep household energy usage private. Real-Life Insight: My AI routines learned that no one uses the living room between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so it automatically adjusts lighting and HVAC, saving energy without manual input.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Devices not reporting: Check connectivity, firmware, and hub integration. Incorrect readings: Calibrate meters or verify device compatibility. Automation not triggering: Review rules and ensure devices are online. Pro Tip: Maintaining logs and regularly reviewing dashboards makes it easier to identify issues and prevent wasted energy.
7. Expanding Your Energy Monitoring System
You can expand by adding more smart plugs or meters, integrating HVAC and lighting, using AI for multi-zone management, and combining with home solar systems for smart energy distribution. Human Insight: Integrating solar panel monitoring with smart plugs allowed me to prioritize solar energy use and minimize grid consumption during the day.
8. Safety Considerations
Always follow electrical safety guidelines, use certified devices, avoid overloading circuits, and keep software and firmware updated to maintain system reliability. Practical Tip: Label all meters and plugs during installation to simplify troubleshooting and future expansions.
9. FAQ – DIY Smart Energy Monitoring
Q1: Can I monitor all devices in my home? A: Yes, with enough smart plugs and circuit-level meters.
Q2: Do I need technical skills? A: Basic monitoring is simple; advanced AI-driven routines may require configuration.
Q3: How much money can I save? A: Depending on usage and automation, savings often range from 10–30%.
Q4: Can AI detect faulty appliances? A: Yes, abnormal consumption patterns can indicate malfunctions.
Q5: Is remote monitoring possible? A: Yes, via apps or hub dashboards accessible from mobile devices.
Conclusion
DIY smart energy monitoring provides real-time insights, actionable automation, and long-term cost savings. With proper hardware, AI integration, and practical planning, you can create an efficient, sustainable, and future-ready smart home energy system. Start with key appliances, expand gradually, and let automation handle the rest.