Advanced Smart Home Automation: Create a Fully Integrated Home System in 2026
Advanced Smart Home Automation: Create a Fully Integrated Home System in 2026
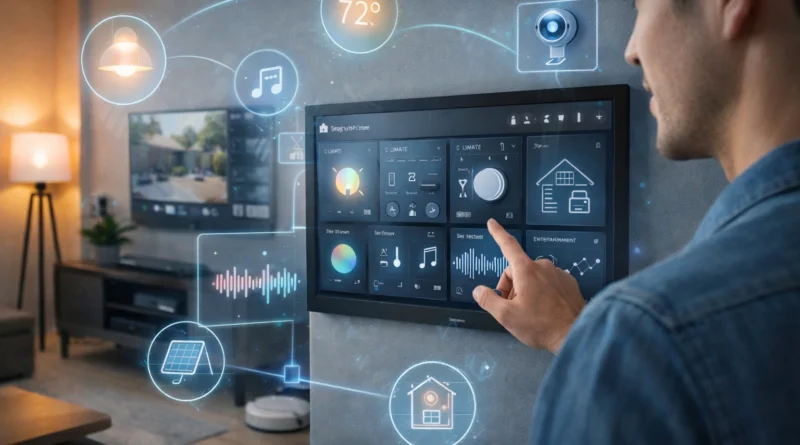
As technology advances, smart homes are becoming more sophisticated than ever. A fully integrated DIY smart home allows you to control lighting, climate, security, entertainment, and energy consumption from a single interface. In my Tunis apartment, I started with a simple smart plug and a couple of sensors, but once I linked all devices into a central hub, I could monitor and automate everything from my phone. Within the first month, energy savings were noticeable, and managing daily routines became effortless. This guide covers essential hardware, software, setup, troubleshooting, advanced automation, AI integration, and practical tips from real-life experience.
1. Understanding Fully Integrated Home Automation
A fully integrated system connects all devices to communicate seamlessly. Benefits include centralized control from a hub or mobile app, advanced automation scenarios based on behavior, time, or environment, energy monitoring, and improved security through coordinated alerts. Local, cloud-based, or hybrid setups can be chosen depending on privacy preferences. In my setup, I used a hybrid approach: most routines run locally, while security notifications go through cloud services, allowing me to monitor the home even while traveling.
2. Essential Hardware Components
Reliable hardware ensures smooth operation. Key components include a single-board computer or mini PC (Raspberry Pi 4, Intel NUC), smart sensors for motion, temperature, humidity, door/window, and water leaks, smart devices like lights, thermostats, locks, and cameras, connectivity modules (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, Ethernet), a control interface (touchscreen or mobile device), and power backup like a UPS or battery system. Pro Tip: modular devices simplify upgrades. In my experience, using a low-quality power supply caused unexpected reboots, which were resolved by upgrading to a stable unit.
3. Software Platforms for Integration
Choose software that supports multiple devices and advanced automation: Home Assistant (open-source, AI integration, customizable dashboards), OpenHAB (modular, for complex setups), Domoticz (lightweight), or Node-RED (visual programming). Installation steps: install the OS on your device, set up the hub software, connect smart devices, and configure automation rules and dashboards. In practice, pairing devices can be tricky initially, but following community guides helped avoid common pitfalls.
4. Advanced Automation Scenarios
Automation routines increase convenience and efficiency. Examples from my home: morning routines with gradual lighting and thermostat adjustments, vacation mode with simulated presence and security alerts, energy-saving routines that auto-adjust heating/cooling and lights, and security automation with motion-activated cameras and smart locks. Tip: always test routines individually before combining multiple automations to prevent conflicts.
5. AI and Predictive Home Automation
AI transforms a smart home into a predictive environment. Voice assistants (Mycroft AI, Alexa, Google Assistant) allow hands-free control, while predictive AI learns habits to adjust lights, climate, and security automatically. AI alerts notify unusual energy use or maintenance needs. Privacy Tip: using local AI models reduces cloud dependency and enhances data security. In my experience, the system learned to turn off unused lights, saving electricity weekly.
6. Integrating Entertainment and Multimedia
Smart TVs, speakers, and streaming devices can integrate into the hub for schedule- or voice-based control. Personalized routines for family members are possible. Practical Tip: ensure devices support protocols like HDMI-CEC or smart plugs to avoid integration issues.
7. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Automation reduces waste. Smart thermostats adjust based on occupancy, lights turn off in empty rooms, smart irrigation saves water, and solar panels can integrate with energy monitoring dashboards. Practical Tip: track usage to optimize costs and environmental impact. My home’s energy bills dropped noticeably after automating lighting and heating based on occupancy.
8. Security and Safety Measures
A secure system includes smart cameras, motion sensors, door/window contacts, automated alerts for emergencies, and remote monitoring via secure apps. Enable encryption and two-factor authentication. In practice, having remote alerts allowed me to detect and fix a water leak before it caused damage.
9. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues include devices not responding (check network and firmware), automation conflicts (review rules and logs), and AI voice recognition failures (check microphones and settings). Maintaining a system log saves hours in diagnosis.
10. Future-Proofing Your Smart Home
Choose open-source or modular platforms, use widely adopted communication standards (Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi 6), keep spare components, and back up configurations. A future-proof system adapts to new devices without a complete rebuild.
11. FAQ – Fully Integrated Smart Home
Q1: Do I need programming experience?
A: Basic knowledge helps, but visual tools simplify setup.
Q2: Can I integrate older devices?
A: Yes, with proper adapters or bridges.
Q3: How much does a full system cost?
A: $500–$2000 depending on devices and AI features.
Q4: Is AI integration necessary?
A: Not mandatory, but enhances automation.
Q5: Can I control everything remotely?
A: Yes, through secure mobile apps, VPN, or cloud services.
Conclusion
A fully integrated DIY smart home maximizes convenience, energy efficiency, and security. With modular hardware, AI integration, and practical planning, you can create a future-ready system that adapts to your lifestyle. Start small, expand gradually, and enjoy the tangible benefits of automation.